Abstract:
Choosing between an Active Optic Cable and a Passive Optical Cable can shape your network’s performance. This article breaks down their tech and use cases for clarity.
What Is an Active Optic Cable?
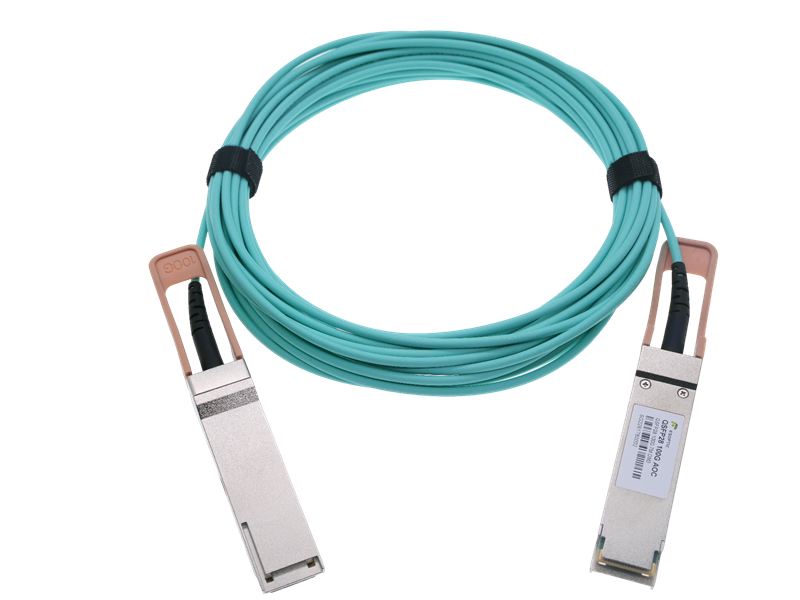
Picture a cable that’s more than just a connector—an Active Optic Cable is a high-speed solution with built-in smarts. It integrates optical transceivers at each end, converting electrical signals to light and boosting them for reliable transmission. Often used in data centers, an Active Optic Cable can stretch up to 100 meters or more, delivering speeds like 40Gbps or 100Gbps. It’s a lightweight, flexible choice for setups needing a little extra power to keep data flowing smoothly.
Understanding the Passive Optical Cable
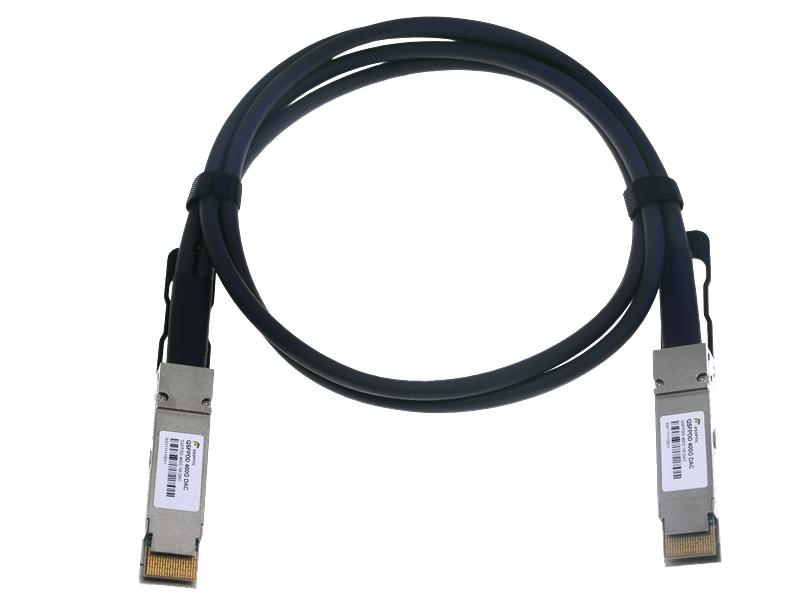
On the flip side, a Passive Optical Cable keeps things simple. It’s a fiber optic link without any active electronics—just pure glass to carry light signals between devices. Think of it as a direct, no-frills connection, typically capping out at 7-10 meters. A Passive Optical Cable shines in short-range scenarios, like linking servers in a rack, where cost and ease outweigh the need for amplification. It’s the minimalist’s pick in optical networking.
Comparing Performance: Active vs Passive
So, how do these stack up? An Active Optic Cable excels over longer distances, thanks to its signal-enhancing tech—perfect for sprawling setups. Meanwhile, a Passive Optical Cable holds its own in tight spaces, offering lower power use and no need for extra hardware. Speed-wise, both can hit high marks, but the active version handles heavier loads over greater reaches. It’s about matching the cable to your network’s layout and goals.
When to Choose Each Cable Type
Picking between an Active Optic Cable and a Passive Optical Cable comes down to your needs. Go active if you’re bridging equipment across a room or building—its boosted signal keeps performance steady. Opt for passive when you’re wiring up a compact cluster, like a single rack, and want to save on cost and energy. Both are plug-and-play, but knowing your distance and bandwidth demands makes the choice a breeze. It’s practical tech tailored to real-world use.
Why These Cables Matter in Modern Networks
The rise of cloud computing and 5G has made options like the Active Optic Cable and Passive Optical Cable more relevant than ever. They’re built to handle the data surge, whether it’s a short hop or a longer haul. Active cables push the boundaries of distance and speed, while passive ones keep things lean and efficient. Together, they’re shaping a flexible, future-ready optical landscape—quietly powering the connections we rely on every day.
Summary:
Active Optic Cable and Passive Optical Cable offer distinct strengths for networking. One boosts signals over distance, the other keeps it simple and close—both are key to today’s tech.
FAQs About Active and Passive Optical Cables
Q: How far can an Active Optic Cable reach?
A: Up to 100 meters or more, depending on the spec.
Q: Is a Passive Optical Cable cheaper?
A: Yes, it’s typically more budget-friendly due to its simplicity.
Q: Can both cables support 100Gbps?
A: Absolutely, though active cables manage it over longer runs.
Q: Which is better for a small setup?
A: A Passive Optical Cable—ideal for short, tight spaces.
Q: Do I need special gear for an Active Optic Cable?
A: Nope, it’s pre-terminated and ready to plug in.